前言
学习了这么久的 web 技术,让我们来复习回顾一下其中的重要知识。内容比较主观,仅为个人理解!
学习笔记列表:
WEB 基础
对于 WEB 技术,我们首先要掌握它的一些基础概念,下面是一些重要概念。
具体部分可以看:
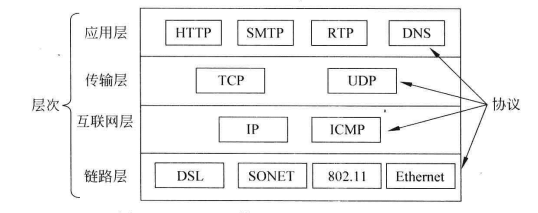
首先,WEB 的根本(web essentials)是建立在 TCP/IP 协议的基础上,一种客户端-服务器端编程架构的网络应用。TCP/IP 的层次结构如下:
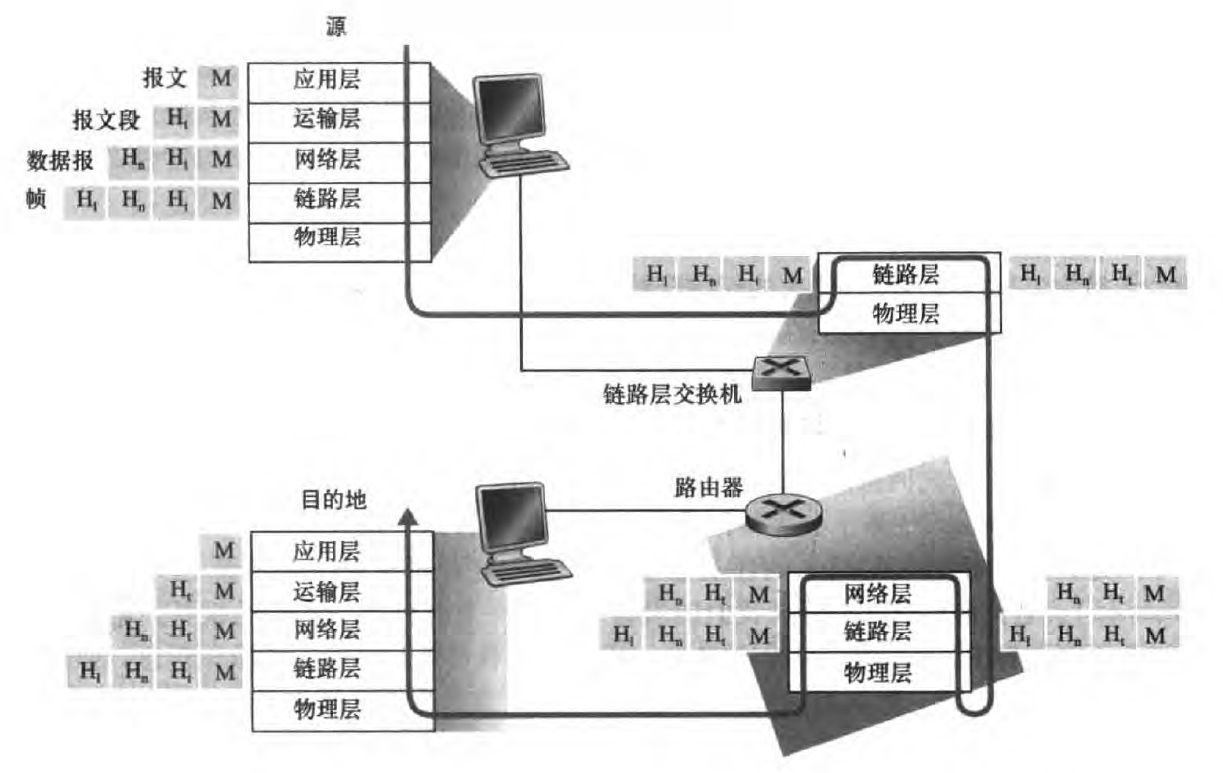
网络访问传输过程:
-
What is the whole process that Telnet simulates Web Client to access Web server?
Telnet 模拟 Web 客户端访问 Web 服务器的整个过程是怎样的?
(下面过程仅为个人答案,答案正确性不作保证!!!)- Telnet 客户端首先需要将 Web 服务器的域名解析为 IP 地址,它使用 DNS 协议在客户端和 DNS 服务器之间在 应用层 进行通信。
The Telnet client needs to resolve the domain name of the web server into an IP address. It uses the DNS protocol to communicate in the application layer between the client and DNS server. - Telnet 客户端在 传输层 使用 TCP 协议与 Web 服务器建立连接。
The Telnet client uses the TCP protocol in the transport layer to establish a connection with the web server. - Telnet 客户端在 应用层 向 Web 服务器发送 HTTP 请求,请求特定的资源。HTTP 协议基于 TCP 协议,数据包首先通过 HTTP 协议传输到传输层,再通过 TCP 协议 传输到 网络层。
The Telnet client sends an HTTP request to the web server for a specific resource in the application layer. The data packet is first transmitted through the HTTP protocol to the transport layer and then through the TCP protocol to the network layer. - IP 协议会为 TCP 数据包添加源和目标 IP 地址,数据包被封装成数据帧并发往网络。
The IP protocol adds the source and destination IP addresses to the TCP data packet, which is encapsulated into a data frame and transmitted onto the network. - 数据帧在 网络接口层(链路层) 被转换成电子信号,并通过 物理层 的电缆、网卡等物理设备传输到 Web 服务器。
The data frame is converted into an electronic signal at the network interface layer (Link layer) and transmitted to the web server through physical devices such as cables and network cards in the physical layer.
- Telnet 客户端首先需要将 Web 服务器的域名解析为 IP 地址,它使用 DNS 协议在客户端和 DNS 服务器之间在 应用层 进行通信。
-
In the web application, what are the primary tasks of a web browser?
在网络应用中,网络浏览器的主要任务是什么?
对于网络浏览器,它的主要任务一般有如下三点:- 将网址 (URL) 转换为 HTTP 请求;
Convert web addresses (URL’s) to HTTP requests; - 通过 HTTP 与 Web 服务器通信;
Communicate with web servers via HTTP; - 呈现(适当地显示)服务器返回的文档。
Render (appropriately display) documents returned by a server.
- 将网址 (URL) 转换为 HTTP 请求;
-
In the web application, what are the basic functionalities of a web server?
在网络应用中,网络服务器的基本功能是什么?- 通过 TCP 接收 HTTP 请求;
Receive HTTP request via TCP; - 将 Host 头映射到特定的虚拟主机(共享一个 IP 地址的许多主机名之一);
Map Host header to specific virtual host (one of many host names sharing an IP address); - 将 Request-URI 映射到与虚拟主机相关的特定资源上;
Map Request-URI to specific resource associated with the virtual host - 文件:在 HTTP 响应中返回文件;
File: Return file in HTTP response - 程序:运行程序并在 HTTP 响应中返回输出;
Program: Run program and return output in HTTP response - 将资源的类型映射到适当的 MIME 类型,设置 Content-Type;
Map type of resource to appropriate MIME type and set Content-Type header; - 记录关于请求和响应的信息。
Log information about the request and response。
- 通过 TCP 接收 HTTP 请求;
-
In the web application, what are the typical browser-server interactions?
在网络应用中,经典的浏览器-服务器交互过程:- 用户在浏览器中输入 Web 地址;
User enters Web address in browser; - 浏览器通过 DNS 解析出服务器的 IP 地址;
Browser uses DNS to locate IP address; - 浏览器与服务器之间开启 TCP 连接;
Browser opens TCP connection to server; - 浏览器通过 TCP 连接向服务器发送 HTTP 请求;
Browser sends HTTP request over connection; - 服务器通过 TCP 连接向浏览器客户端发送 HTTP 响应;
Server sends HTTP response to browser over connection; - 浏览器在可视区展示响应内容。
Browser displays body of response in the client area of the browser window。
- 用户在浏览器中输入 Web 地址;
JavaScript
JavaScript 数组排序
JavaScript 的数组中的 sort() 排序方法和 C/C++ 的 qsort 很像,它的其中一个参数是一个比较函数。
sort() 是 Array 对象的一个方法,对数组的元素进行排序,并返回数组。格式为:
sort() // orsort(compareFn)如果没有指明 compareFn,那么元素会按照 转换为的字符串的诸个字符的 Unicode 位点进行排序(逐位字典序)。
如果指明了 compareFn,compareFn 只接受返回值存在 < 0、> 0 或 === 0 的情况。数组会按照调用该函数的返回值排序。即 a 和 b 是两个将要被比较的元素:
- 如果
compareFn(a, b) > 0,b 会被排列到 a 之前; - 如果
compareFn(a, b) < 0,a 会被排列到 b 之前; - 如果
compareFn(a, b) === 0,相对位置不变; - 比较函数需对相同输入返回稳定结果。
总结:在
compareFn函数 返回 1 的时候,表示b应该排在a的前面。sort方法仅当且仅当比较函数返回 1 时会交换两个元素的位置。
我们的比较函数可以分成四种情况:数字升序、数字降序、字符串字典序、字符串逆字典序。
数字升序 (ascending order)
function compareNumbersAscending(a, b) { return a - b;}等价标准写法:
function compareClassic(a, b) { if (a > b) return 1; else if (a === b) return 0; else return -1;}注意:数字的升序不能使用无比较函数的形式!无比较函数为逐位字典序,不一定等于数字升序。
示例:
function compareNumbers(a, b) { return a - b; }var A = [80, 9, 4, 66];console.log("function: " + A.sort(compareNumbers)); // 4,9,66,80console.log("nonfunction: " + A.sort()); // 4,66,80,9(错误)数字降序 (descending order)
function compareNumbersDescending(a, b) { return compareNumbersAscending(b, a);}或直接:
function compareNumbersDescending(a, b) { return b - a;}字符串字典序 (alphabetical order)
无比较函数即可:A.sort()。
字符串逆字典序 (alphabetical reverse order)
function dec_order(a, b) { if (a > b) return -1; else if (a < b) return 1; else return 0;}JavaScript 对象参数传递
在 JavaScript 中,如果变量代表一个对象,那么存储在该变量中的内容 就是一个指向该对象的引用(指针),而不是对象本身。赋值与传参均为引用。
var o1 = new Object();o1.data = "original";var o2 = new Object();o2.data = "original";
objArgs(o1, o2);function objArgs(param1, param2) { // Change the data in param1 and its argument param1.data = "changed"; // Change the object referenced by param2, but not its argument param2 = param1;
window.alert("param1 is " + param1.data + "\n" + "param2 is " + param2.data); return;}
// 离开函数后再次检查window.alert("o1 is " + o1.data + "\n" + "o2 is " + o2.data);上面逻辑:修改 param1.data 会影响到 o1;param2 = param1 仅改变了 param2 的引用指向,不影响 o2 的原始对象。
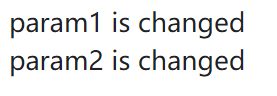

正则表达式
正则表达式是表示一组字符串的某种方式,可以看成是这一组字符串的集合。
在 JavaScript 中创建正则表达式有两种方法:
RegExp()构造函数- 正则表达式字面量
/.../
示例(匹配「三个数字」):
var acTest1 = new RegExp("^\\d\\d\\d$");var acTest2 = /^\d\d\d$/;RegExp 对象有 test(areaString) 布尔方法,用于检测匹配:
var acTest = new RegExp("^\\d\\d\\d$");if (!acTest.test(areaCode)) { window.alert(areaCode + " is not a valid area code.");}一般使用 ^ 表示开头,$ 表示结尾,\\b 表示单词边界。常用限定符如下:
| 限定符 | 描述 |
|---|---|
* | 匹配前一个元素 0 次或多次 |
+ | 匹配前一个元素 1 次或多次 |
? | 匹配前一个元素 0 次或 1 次 |
{n} | 匹配前一个元素恰好出现 n 次 |
{n,} | 匹配前一个元素至少 n 次 |
{n,m} | 匹配前一个元素至少 n 次,不超过 m 次 |
使用一个 RegExp 实例,编写一个 JavaScript 函数
isValid(),它接受一个 String 参数,如果该参数与下列电话号码格式之一匹配,就返回 true;否则返回 false。
(123)456-7890
(123) 456-7890
123/456-7890
123-456-7890
123 456 7890
1234567890
通用正则表达式(示例):
var valid = /^(\(?\d{3}\)?)[ -\/]?\d{3}[- ]?\d{4}$/;或分组更清晰的写法:
var valid = /^((\(\d{3}\))|\d{3})[ -\/]?\d{3}[- ]?\d{4}$/;Java Servlet & Session
Servlet 用于客户端与服务器端的交互。
在 Web 应用中,Session 是一种服务器端技术(由服务器存储),用于 跟踪用户在不同页面和请求之间的状态。服务器为每个会话创建唯一的 session ID 与会话数据关联(登录状态、购物车、偏好等)。
创建或获取 Session:
HttpSession session = request.getSession();- 当 HTTP 请求不包含有效 session ID 时,服务器会创建
HttpSession、分配 session ID;getSession()返回新建对象; - 当请求包含有效 session ID 时,返回已存在的
HttpSession; - 可通过
session.isNew()判断是否为新会话。
更详细内容见:
https://hoyue.fun/web_6.html#Sessions
CSS
在 CSS 中,层叠 与 优先级 是最重要的概念。当两条规则冲突时,浏览器依据优先级与书写顺序决定最终样式。
基本规则:
- 当应用两条 同级别 的规则到一个元素时,写在后面的规则生效。
- 选择器优先级(从低到高):
通用选择器(*) < 类型选择器(如h1)、伪元素(如::before) < 类选择器(.example)、属性选择器([type="radio"])、伪类(:hover) < ID 选择器(#id) < 内联样式(style="...")。 - 一些属性可继承:当子元素的 继承属性 未指定时,取父元素的计算值。
示例题(两条声明):
background-color: silver;font-size: larger;将称为“背景声明”和“文本声明”。
(a) 将背景声明应用于 div,文本声明应用于 strong:
div { background-color: silver; }strong { font-size: larger; }(b) 使用单个规则,同时应用于 p 与 em(逗号分隔):
p, em { background-color: silver; font-size: larger; }(c) 将背景声明应用于 id 为 Nevada 的元素和 class 为 shiny 的元素:
#Nevada, .shiny { background-color: silver; }(d) 将文本声明应用于属于 bigger 类的 span 元素:
span.bigger { font-size: larger; }/* 或 */.bigger span { font-size: larger; }(e) 将文本声明应用于属于其他 span 元素后代的 span 元素:
span span { font-size: larger; }(f) 当光标悬停在超链接上时应用背景声明(伪类选择器):
a:hover { background-color: silver; }DOM 技术
用于客户端与浏览器的交互,一般用于对用户动作做出反馈(如鼠标移动等):
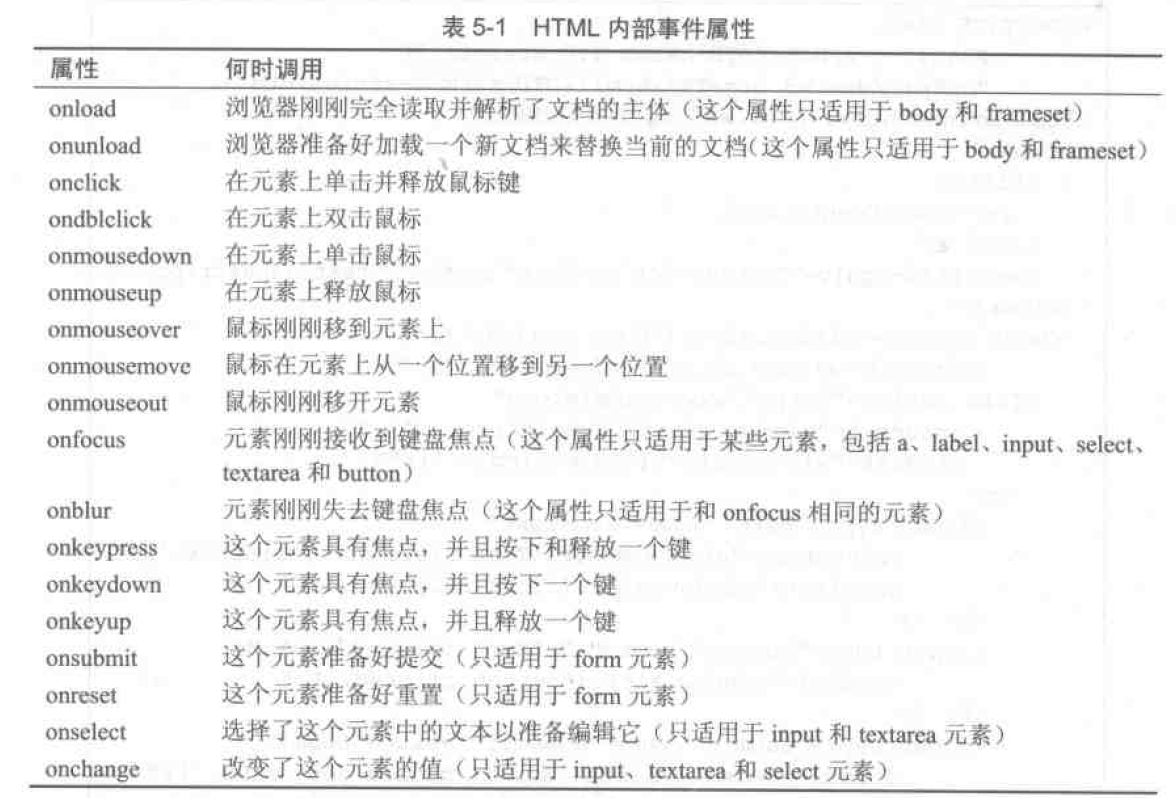
在使用 内部事件属性 之前,必须在文档的 head 中包含一个 meta 元素,用于为文档内的脚本指定默认语言;content="text/javascript" 告诉浏览器脚本语言为 JavaScript:
<meta http-equiv="Content-Script-Type" content="text/javascript" />我们在 HTML 中设置内部事件属性,并在 JavaScript 中定义函数用于交互。具体例子请见:

